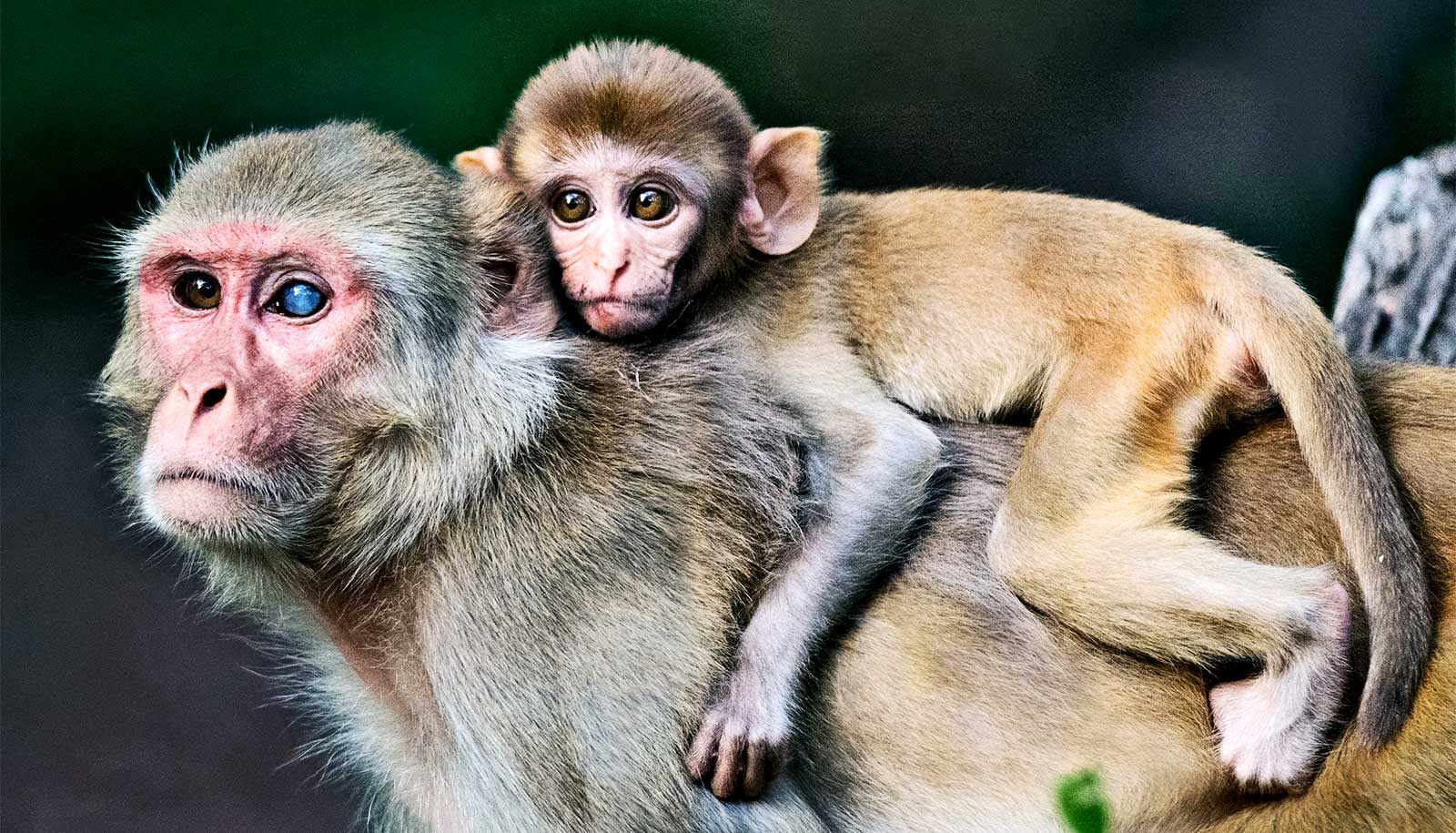
Zika virus infection soon after birth leads to long-term brain and behavior problems, according to research with rhesus monkeys.
The brain and behavior problems include persistent socioemotional, cognitive, and motor deficits, as well as abnormalities in brain structure and function.
More than 85 countries and territories have reported evidence of mosquito-acquired Zika virus infection, for which there is no cure or medications to treat it. Zika virus and the mosquitoes that transmit it have not been eliminated, so transmission remains a risk.
“Researchers have shown the devastating damage Zika virus causes to a fetus, but we had questions about what happens to the developing brain of a young child who gets infected by Zika,” says lead researcher Ann Chahroudi, an affiliate scientist in the Division of Microbiology and Immunology at Yerkes National Primate Research Center and an associate professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Emory University School of Medicine.
“Our pilot study in nonhuman primates provides clues that Zika virus infection during the early postnatal period can have long-lasting impact on how the brain develops and works, and how this scenario has the potential to impact child behavior,” Chahroudi continues.
Neurodevelopmental changes
The study, published online in Nature Communications, followed four infant rhesus monkeys for one year after Zika virus infection at one month of age. Studying a rhesus monkey until the age of one translates to the equivalent of four to five years in human age.
Researchers found postnatal Zika virus infections led to impairments in memory function, significant changes in behavior, including reduced social interactions and increased emotional reactions, and some gross motor deficits. These changes corresponded with structural and functional brain changes the researchers found on MRI scans—findings that indicate long-term neurological complications.
“Our findings demonstrate neurodevelopmental changes detected at three and six months of age are persistent,” says first author Jessica Raper, research assistant professor at Yerkes. “This is significant because it gives healthcare providers a better understanding of possible complications of Zika beyond infection during pregnancy and into the first years of life,” she continues.
What about human brains?
Considering the similarities between human and nonhuman primate brain development, the rhesus monkey provides an important translational model for understanding the impact of viral infection on the human brain. While the infant brain has an extended development period that may facilitate healing after early brain damage, the current study found persistent alterations in brain growth and function as a result of the early postnatal Zika virus infection.
The research was part of a pilot program at Yerkes. The program serves to generate initial, proof-of-concept data that will inform future studies. “Our results shed light on potential outcomes of human infants infected with Zika virus after birth and provide a platform to test treatments to alleviate long-term neurologic consequences of Zika infection,” says Chahroudi. “Our research team encourages future studies to understand the impact of early postnatal Zika infection during later stages of life, from adolescence to adulthood.”
The collaborative research team included researchers from Yerkes and Emory, Howard University, and UNC Chapel Hill.
Source: Emory University