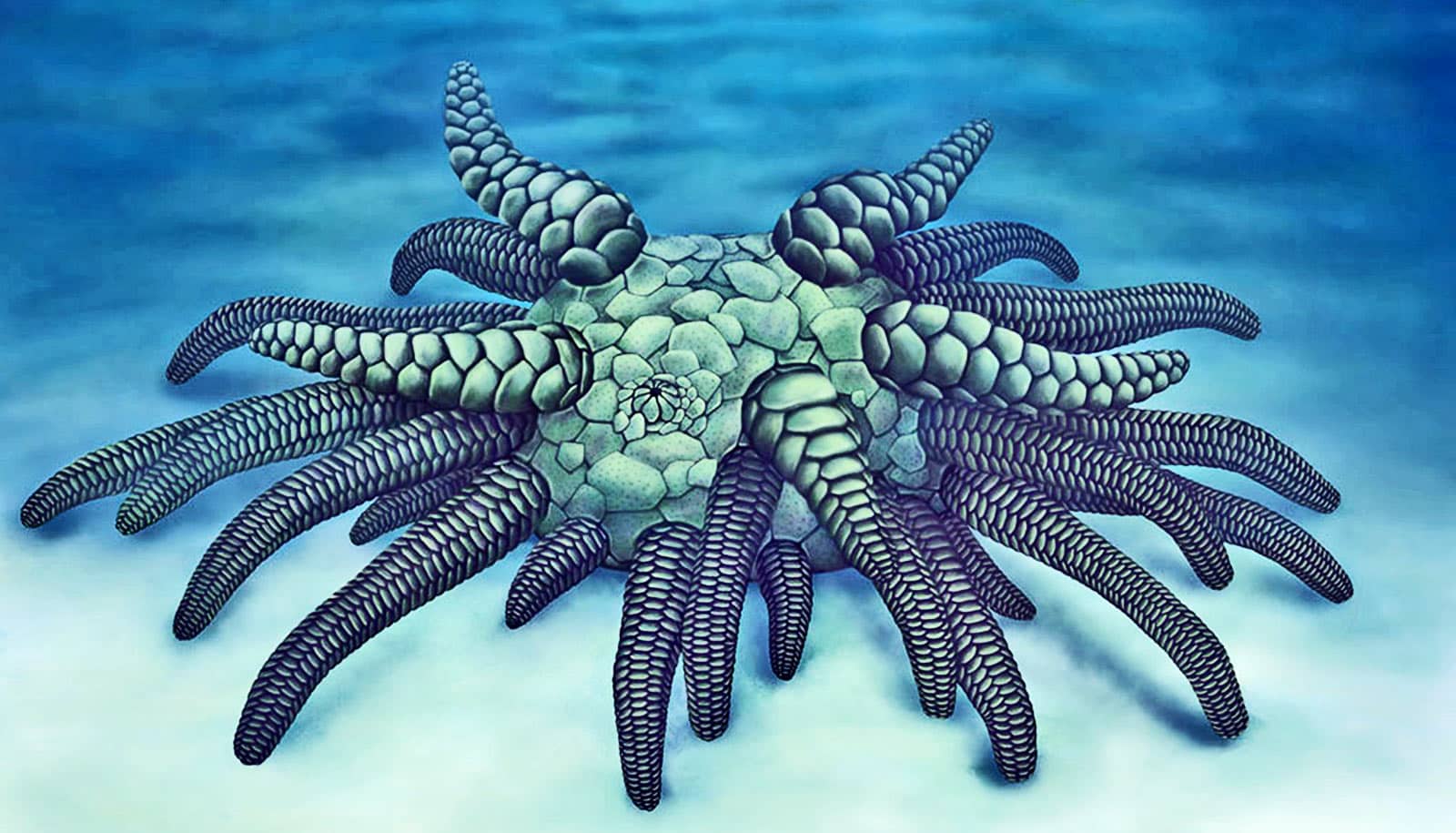
Researchers have identified a 430 million-year-old fossil as a new species related to living sea cucumbers.
They named the creature Sollasina cthulhu, after HP Lovecraft’s tentacled monster, Cthulhu.
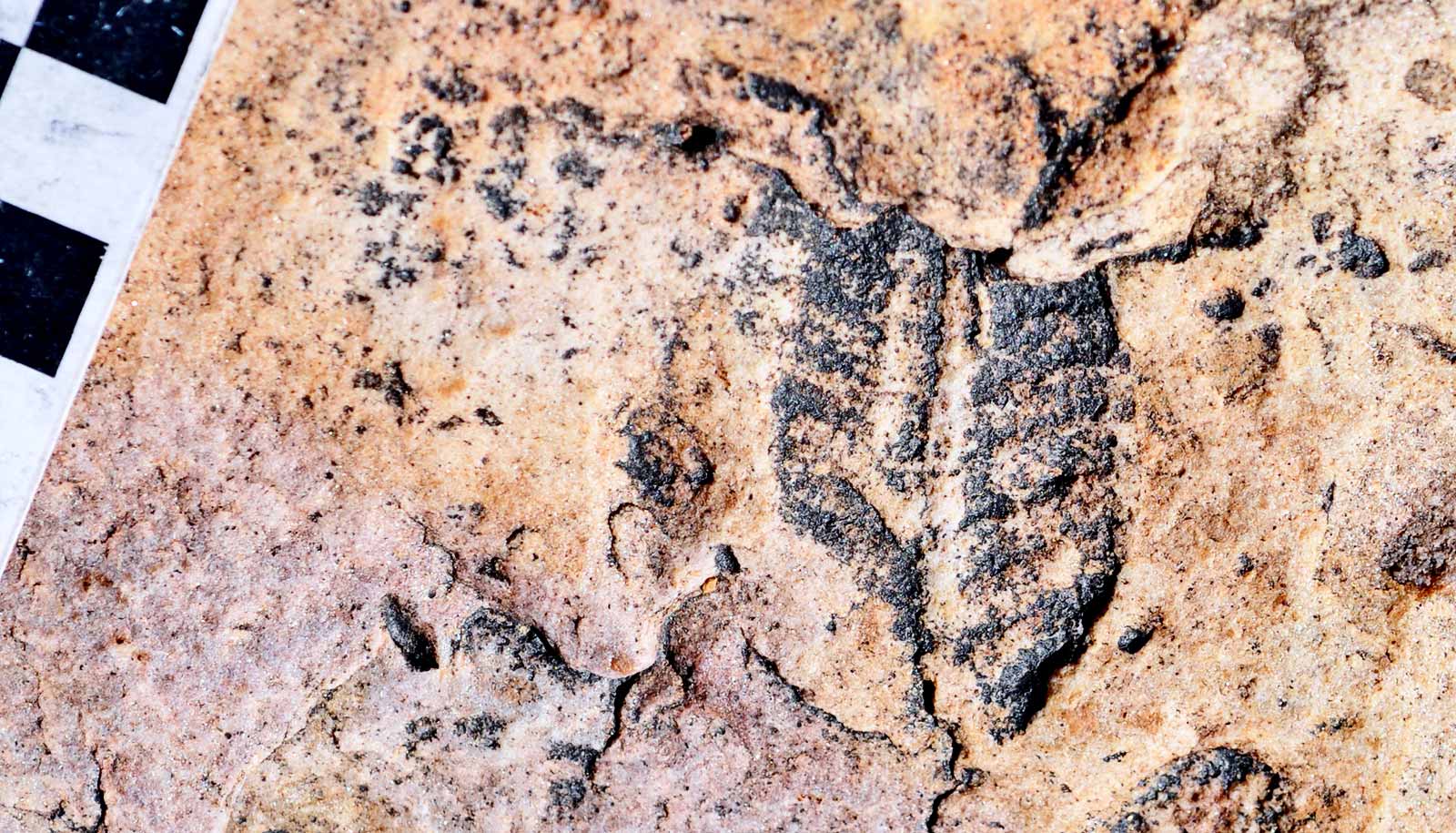
The creature had 45 tentacle-like tube feet, which it used to crawl along the ocean floor and capture food—and was small, about the size of a large spider. Scientists found it in the Herefordshire Lagerstätte in the United Kingdom, a site that has proven to be a trove of fossilized ancient sea animals.
“In this paper, we report a new echinoderm—the group that includes sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sea stars—with soft-tissue preservation,” says coauthor Derek Briggs, a paleontologist at Yale University.
“This new species belongs to an extinct group called the ophiocistioids. With the aid of high-resolution physical-optical tomography, we describe the species in 3D, revealing internal elements of the water vascular system that were previously unknown in this group and, indeed, in nearly all fossil echinoderms.”
The 3D reconstruction process involves grinding a fossil away, layer by layer, and taking photographs at each stage. This results in hundreds of slice images, which scientists then digitally reconstruct into a “virtual fossil.”
That’s how the researchers were able to discern Sollasina’s internal water vascular system and determine it is more closely related to sea cucumbers rather than to sea urchins.
“The water vascular system operates the tentacle-like structures that they used for locomotion and food capture,” Briggs says.
“The tube feet of living echinoderms are naked, but in the ophiocistioids they were plated. Our analysis strongly suggests that ophiocistioids diverged from the line leading to modern sea cucumbers.”
The researchers says Sollasina’s existence demonstrates that the sea cucumber skeleton modified gradually during the assembly of its body plan.
A study announcing the discovery appears in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Additional coauthors came from Oxford University, the University of Leicester, Imperial College London, and University College London. The Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History Invertebrate Paleontology Division, the Oxford University Museum of Natural History, the John Fell Oxford University Press Research Fund, the Natural Environment Research Council, and the Leverhulme Trust supported the research.
Source: Yale University