In a new study, researchers found no evidence of early onset dementia in a small sample of retired professional hockey and football players.
The new research adds important information to the body of knowledge about the cognitive and behavioral status of retired athletes who spent their careers in contact sports.
“We don’t deny that CTE exists in some former athletes… The larger question is, how prevalent is the problem?”
The researchers assessed 21 professional athletes retired from the National Football League and the National Hockey League on neuropsychological measures associated with mild cognitive impairment and executive function.
The researchers have published four papers in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation: an overview paper plus three additional papers assessing cognitive changes, executive function, and advanced brain imaging.
The study, which the researchers note involved “a relatively small sample of former athletes,” did not find evidence of early onset dementia in the retired players, which would be expected with chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). The comprehensive, case-control study is believed to be the first age-matched athlete comparison designed to identify in retired living athletes cognitive symptoms or imaging findings that would indicate the presence of early onset dementia.
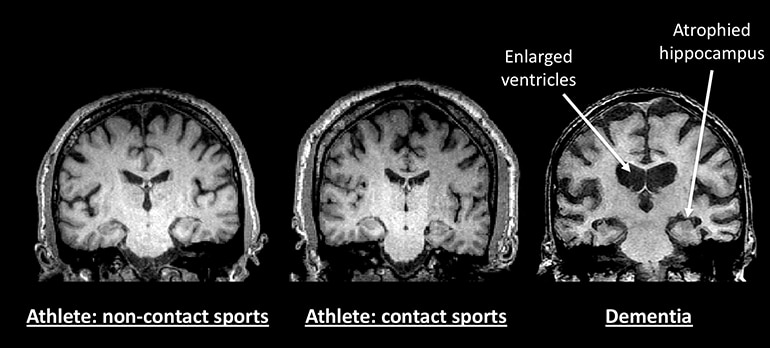
CTE in athletes has been linked to a history of concussive or sub-concussive hits. The researchers’ overview paper notes: “…research to date on CTE based on pathological studies implies that most athletes who played contact sports professionally have a high probability of eventually experiencing CTE.”
Most athletes with CTE damage do experience early onset dementia, although there is also some evidence that it may be possible to have CTE damage without clinical symptoms. The condition can only be diagnosed for certain after death.
No denial of CTE
“We don’t deny that CTE exists in some former athletes,” says lead investigator and paper coauthor Barry S. Willer, professor of psychiatry in the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at the University at Buffalo. “It has been linked to contact sports and concussions that happen while playing those sports, but it’s not a sure thing. The larger question is, how prevalent is the problem?”
The researchers began the study, in part, to address some limitations of previous studies on athletes and CTE. In pathological studies from Boston University, researchers found CTE in the brains of nearly all professional football and hockey players, many of whom had clearly exhibited dementia, and whose brains families donated for study.
The assumption has been that CTE is a result of repetitive concussions and/or non-concussive hits sustained while playing sports. It has also been seen in the brains of much younger individuals. Investigators on these postmortem studies have cited selection bias and the lack of a control group, that is, donated brains from people who didn’t play contact sports, as important limitations.
Testing brain health
In 2013, Willer and his coinvestigator, John Leddy, director of the Concussion Management Clinic and professor of orthopaedics in the Jacobs School, developed a series of assessments that could provide a comprehensive view of the extent to which each athlete was functioning.
“We designed the study so that when we discovered dementia we could also rule out or account for the myriad of other possible explanations for cognitive decline, such as mental health, lifestyle, eating habits, drug and alcohol abuse, and so on,” Willer says.
“Not one [player] qualified as having early onset dementia.”
The case-control study provides the first age-matched athlete comparison designed to identify in retired living athletes cognitive symptoms or imaging findings that would indicate early onset dementia.
The assessments of cognitive function (e.g., memory, attention, visual spatial orientation), executive function, and mental health in the retired athletes didn’t reveal statistically significant impairment compared to controls.
The researchers did find evidence of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in more of the retired athletes than the controls, but says the rate was as expected for the age, education level, and body mass index of the athletes, all factors that can raise the risk of MCI; it also was not statistically significant.
Advanced brain imaging detected no microscopic or macroscopic brain tissue injury differences in retired athletes versus the controls. Researchers found that the non-contact sport athletes had a higher rate of microbleeds in the brain but these results only approached statistical significance.
“We looked at 21 former professional football and hockey players with an average age of 56. Not one qualified as having early onset dementia,” Leddy adds.
He notes that the athletes in the study had played an average of 8 years in their professional leagues, and thus likely had plenty of opportunities to experience concussions. Researchers deemed information from the athletes themselves about how many concussions they remember experiencing unreliable and did not include it in the study.
Finding veteran athletes
To do the study, Willer and Leddy approached the local alumni organizations of the Buffalo Bills and Buffalo Sabres. Representatives of both alumni groups served on the advisory committee of the project.
The researchers found that the athletes had valuable insights on how to frame the research. They also discovered that many athletes were interested in the research, exhibiting concerns that they, themselves, might be showing early signs of dementia.
Biomarker could lead to CTE diagnosis during life
Researchers recruited twenty-one controls who engaged in non-contract sports from local swimming, cycling, and running clubs. These age-matched control athletes were still actively participating in their sport, were significantly better educated and healthier and, on average, weighed 50 pounds less than the retired professional athletes.
Both groups underwent comprehensive neuropsychological testing designed to identify MCI, considered an early sign of dementia. They filled out questionnaires about executive function and personality and underwent advanced brain imaging through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Researchers questioned family members about cognition and personality. Participants also provided information about diet, lifestyle, drug and alcohol use, and cardiovascular risk factors. Researchers took blood samples to assess cholesterol levels. Participants underwent thorough physical exams.
“We did find the former athletes to be quite physically affected…”
A key goal was to try to determine if symptoms signaling CTE, specifically, early-onset dementia, could be seen in retired professional athletes and how they compared with athletes who didn’t play a contact sport. The researchers also wanted to assist former players and their families in addressing changes they were experiencing as a result of aging.
The main finding was that there was no significant difference in brain imaging, cognition, behavior, or executive function between the retired professional athletes and the controls. The biggest health differences that were detected between the professional athletes included significant risk for obesity, chronic pain, orthopedic surgeries, and significant problems with sleep and anxiety.
“We went into this study with the expectation that we’d find any number of former athletes with dementia,” says Leddy. “And while some of the former professional athletes reported concerns that they felt they were experiencing a decline in memory, and other cognitive issues, the study results did not bear this out.
“We did find the former athletes to be quite physically affected,” Leddy says. “Some of them have had knees or hips replaced, many are in chronic pain, they have arthritis, and some are not just overweight but obese.” A number of the athletes also reported sleep apnea.
Willer and Leddy agree that much more research needs to be done, especially on a larger number of living athletes who played a contact sport professionally.
Head injury, not concussion, may cause CTE
Additional coauthors are from Buffalo and Ohio State University. The Ralph C. Wilson, Jr. Foundation funded the new research. Wilson was the founder and owner of the Buffalo Bills until his death in 2014. The foundation did not have a role in selecting subjects, study design, data analysis, or preparation of manuscripts to report findings. Its aim in funding the study was to increase the range of medical services available to retired athletes, including unbiased assessment of signs of early onset dementia. NFL Charities, the philanthropic foundation of the NFL, previously funded Leddy and Willer to determine an objective way to assess when athletes can safely return to play after a concussion.
The Robert Rich Family Foundation also provided funding for the study. The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health supported the research on imaging.
Source: University at Buffalo