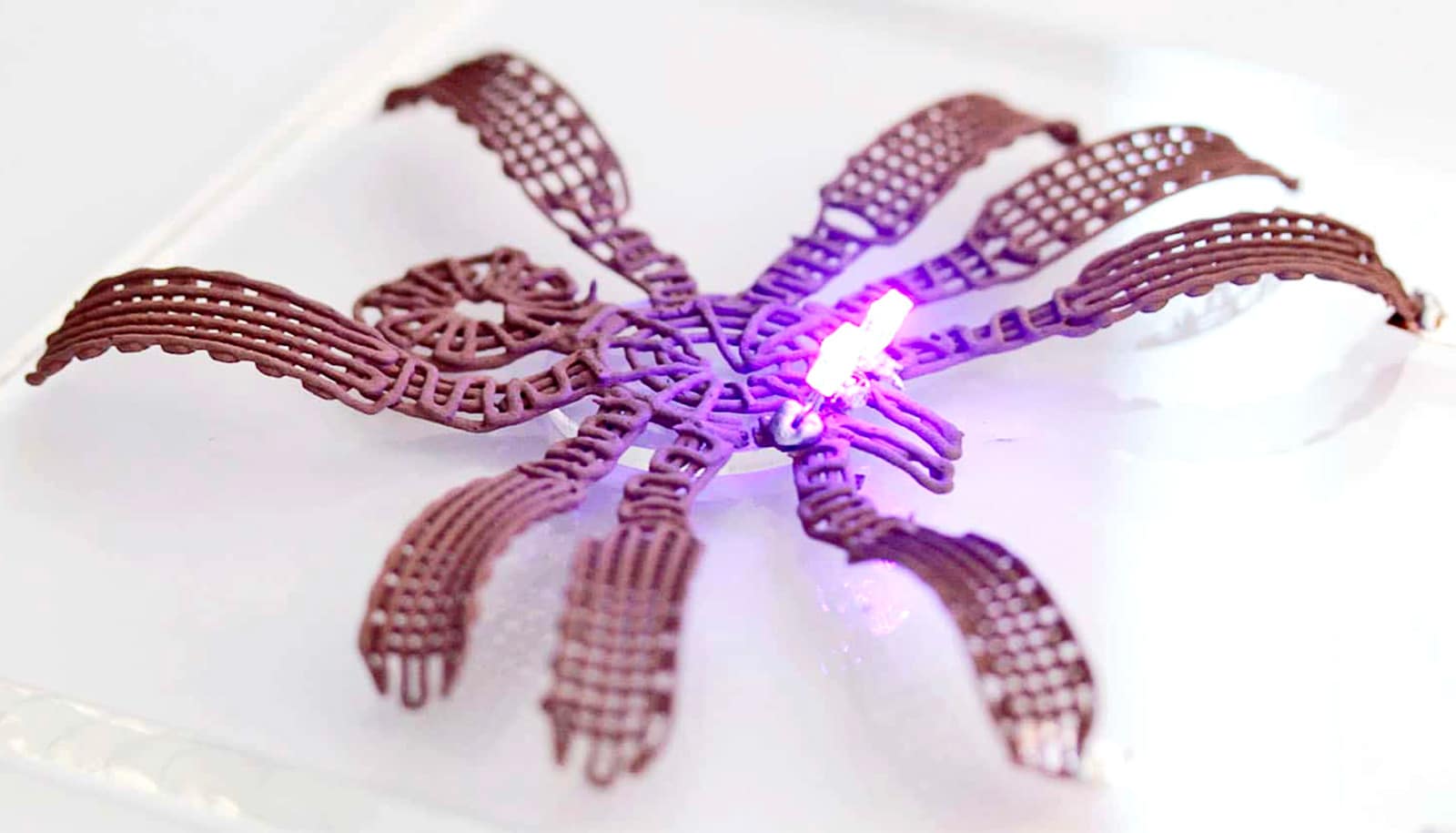
A new metallic gel that is highly electrically conductive can be used to print three-dimensional solid objects at room temperature, researchers report.
“3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing, but we’re not aware of previous technologies that allowed you to print 3D metal objects at room temperature in a single step,” says Michael Dickey, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University and co-corresponding author of the study in the journal Matter. “This opens the door to manufacturing a wide range of electronic components and devices.”
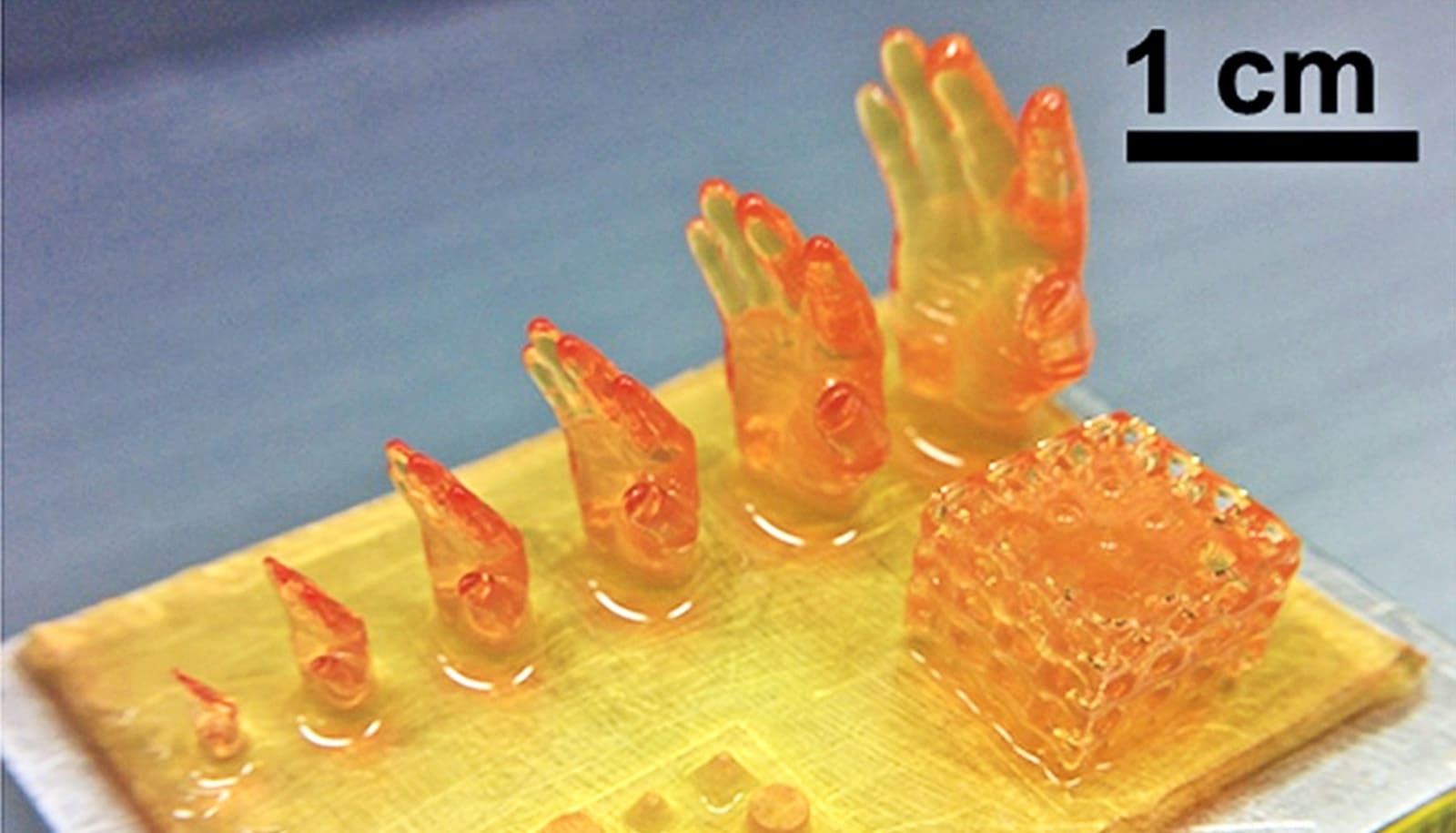
To create the metallic gel, the researchers start with a solution of micron-scale copper particles suspended in water. The researchers then add a small amount of an indium-gallium alloy that is liquid metal at room temperature. The resulting mixture is then stirred together.
As the mixture is stirred, the liquid metal and copper particles essentially stick to each other, forming a metallic gel “network” within the aqueous solution.
“This gel-like consistency is important, because it means you have a fairly uniform distribution of copper particles throughout the material,” Dickey says. “This does two things. First, it means the network of particles connect to form electrical pathways. And second, it means that the copper particles aren’t settling out of solution and clogging the printer.”
The resulting gel can be printed using a conventional 3D printing nozzle and retains its shape when printed. And, when allowed to dry at room temperature, the resulting 3D object becomes even more solid while retaining its shape.
However, if users decide to apply heat to the printed object while it is drying, some interesting things can happen.
The researchers found that the alignment of the particles influences how the material dries. For example, if you printed a cylindrical object, the sides would contract more than the top and bottom as it dries. If something is drying at room temperature, the process is sufficiently slow that it doesn’t create structural change in the object.
However, if you apply heat—for example, put it under a heat lamp at 80 degrees Celsius (176 degrees Fahrenheit)—the rapid drying can cause structural deformation. Because this deformation is predictable, that means you can make a printed object change shape after it is printed by controlling the pattern of the printed object and the amount of heat the object is exposed to while drying.
“Ultimately, this sort of four-dimensional printing—the traditional three dimensions, plus time—is one more tool that can be used to create structures with the desired dimensions,” Dickey says. “But what we find most exciting about this material is its conductivity.
“Because the printed objects end up being as much as 97.5% metal, they are highly conductive. It’s obviously not as conductive as conventional copper wire, but it’s impossible to 3D print copper wire at room temperature. And what we’ve developed is far more conductive than anything else that can be printed. We’re pretty excited about the applications here.
“We’re open to working with industry partners to explore potential applications, and are always happy to talk with potential collaborators about future directions for research,” Dickey says.
Ruizhe Xing, a former visiting scholar at NC State affiliated with Northwestern Polytechnical University and Tianjin University is the paper’s lead author.
Additional coauthors are from the National University of Singapore, Tianjin University, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Taiyuan University of Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, and NC State.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China and the China Scholarship Council funded the work.
Source: NC State