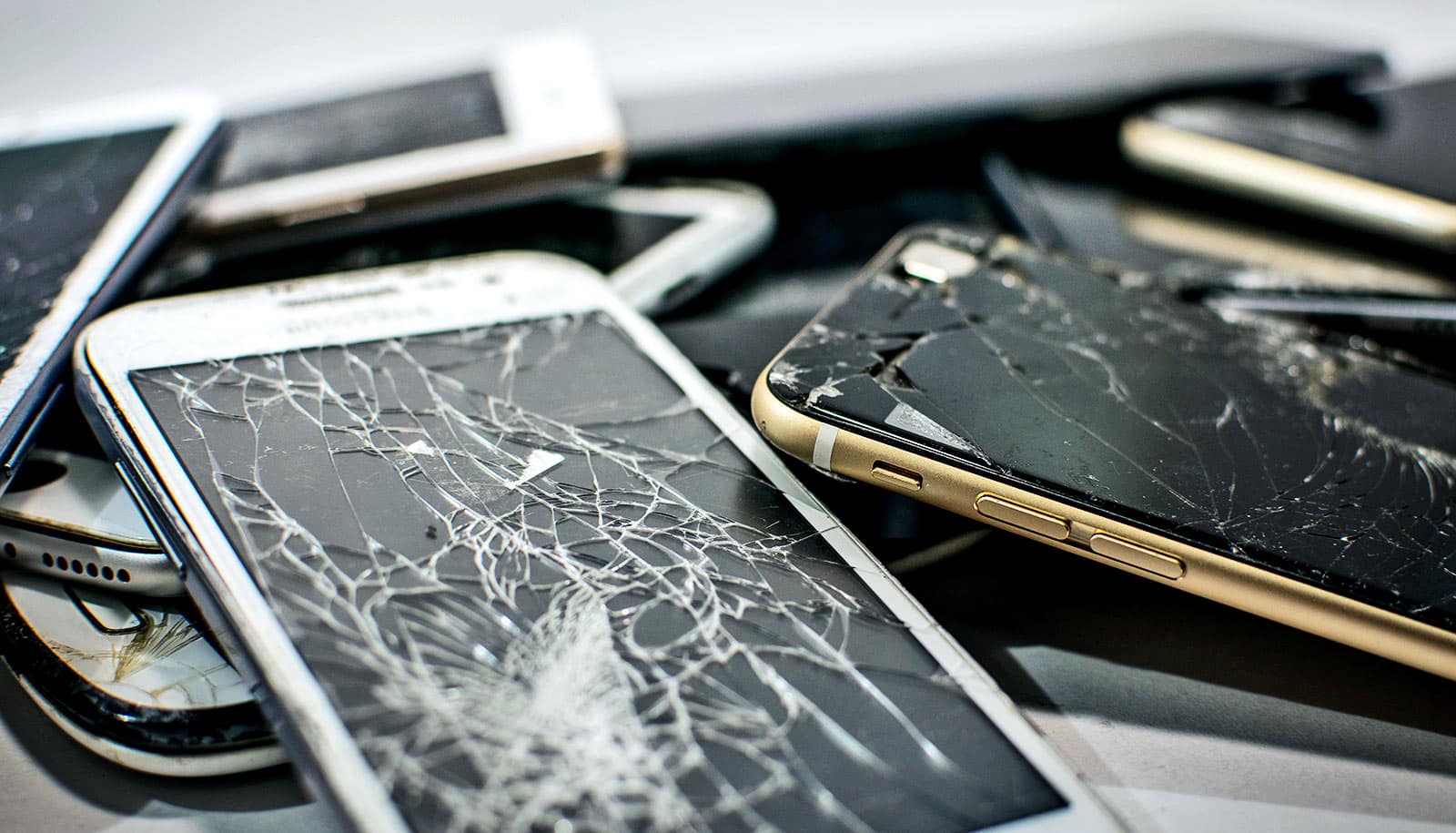
Researchers have recovered gold from electronic waste.
Their highly sustainable new method is based on a protein fibril sponge, which the scientists derive from whey, a food industry byproduct.
Transforming base materials into gold was one of the elusive goals of the alchemists of yore. Now Professor Raffaele Mezzenga from the health sciences and technology department at ETH Zurich has accomplished something in that vein.
He has not, of course, transformed another chemical element into gold, as the alchemists sought to do. But he has managed to recover gold from electronic waste using a byproduct of the cheesemaking process.

Electronic waste contains a variety of valuable metals, including copper, cobalt, and even significant amounts of gold. Recovering this gold from disused smartphones and computers is an attractive proposition in view of the rising demand for the precious metal. However, the recovery methods devised to date are energy-intensive and often require the use of highly toxic chemicals.
Now, a group led by Mezzenga has come up with a very efficient, cost-effective, and above all far more sustainable method: with a sponge made from a protein matrix, the researchers have successfully extracted gold from electronic waste.
To manufacture the sponge, Mohammad Peydayesh, a senior scientist in Mezzenga’s Group, and his colleagues denatured whey proteins under acidic conditions and high temperatures, so that they aggregated into protein nanofibrils in a gel. The scientists then dried the gel, creating a sponge out of these protein fibrils.
To recover gold in the laboratory experiment, the team salvaged the electronic motherboards from 20 old computer motherboards and extracted the metal parts. They dissolved these parts in an acid bath so as to ionize the metals.
When they placed the protein fiber sponge in the metal ion solution, the gold ions adhered to the protein fibers. Other metal ions can also adhere to the fibers, but gold ions do so much more efficiently. The researchers demonstrated this in their paper, which appears in the journal Advanced Materials.
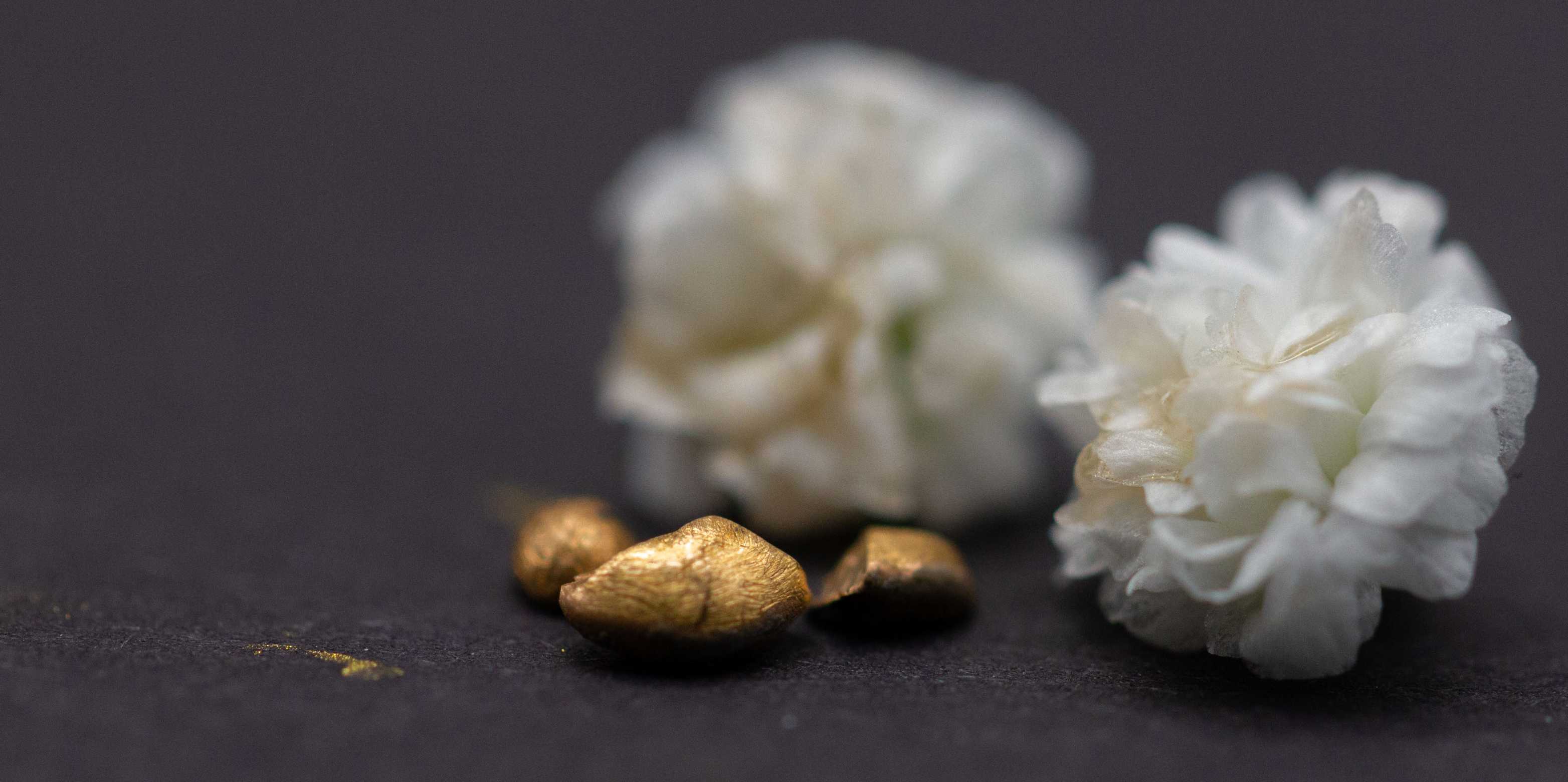
As the next step, the researchers heated the sponge. This reduced the gold ions into flakes, which the scientists subsequently melted down into a gold nugget. In this way, they obtained a nugget of around 450 milligrams out of the 20 computer motherboards. The nugget was 91% gold (the remainder being copper), which corresponds to 22 carats.
The new technology is commercially viable, as Mezzenga’s calculations show: procurement costs for the source materials added to the energy costs for the entire process are 50 times lower than the value of the gold that can be recovered.
Next, the researchers want to develop the technology to ready it for the market. Although electronic waste is the most promising starting product from which they want to extract gold, there are other possible sources. These include industrial waste from microchip manufacturing or from gold-plating processes. In addition, the scientists plan to investigate whether they can manufacture the protein fibril sponges out of other protein-rich byproducts or waste products from the food industry.
“The fact I love the most is that we’re using a food industry byproduct to obtain gold from electronic waste,” Mezzenga says. In a very real sense, he observes, the method transforms two waste products into gold. “You can’t get much more sustainable than that!”
Source: ETH Zurich