Extinct dinosaurs may have rocked pops of color on different parts of their bodies and flashed those colors to entice mates, just like birds do today, a new study shows.
Most birds aren’t as colorful as parrots or peacocks. But if you look beyond the feathers, bright colors on birds aren’t hard to find: Think pink pigeon feet, red rooster combs, and yellow pelican pouches.
“Living birds use an array of pigments and can be very colorful on their beaks, legs, and around their eyes,” says lead author Sarah Davis, a doctoral candidate at the Jackson School of Geosciences at the University of Texas at Austin. “We could expect that extinct dinosaurs expressed the same colors.”
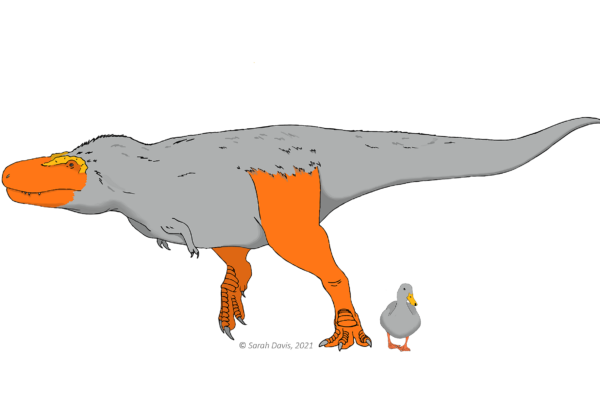
The takeaway on potential dinosaur color schemes comes from broader findings about skin and tissue color in the common ancestor of living birds and extinct dinosaurs, an ancient archosaur that lived near the beginning of the Triassic period.
By analyzing whether bright body color was present in living dinosaur relatives—including turtles, crocodiles, and over 4,000 bird species—the researchers determined that the common ancestor had a 50% chance of having bright colors in the soft tissues of its body.
The bright colors examined in the study typically come from carotenoids—a class of colorful red, orange, and yellow pigments that birds extract from their food. Carotenoids don’t fossilize as well as brown and black pigments, which means scientists must study color in living animals to look for clues about color expression in their extinct ancestors.
The researchers used the data collected from birds and other animals to make phylogenic reconstructions, a scientific method used to investigate the evolutionary histories of species.
The 50% estimate for bright color applies equally to skin, beaks, and scales of the ancient archosaur. In contrast, the research found that there was a 0% chance that claws and feathers were brightly colored, which is consistent with other research, Davis says.
The study also examined the connection between color and a diet high in carotenoids. Davis found that birds with higher carotenoid diets (plant- and invertebrate-rich) were more likely to be colorful than meat eaters. What’s more, she found that plant-eating birds expressed bright colors in more places on their bodies than meat eaters or omnivores.
“The earliest dinosaurs were pony-sized and ate large, vertebrate prey,” says coauthor Julia Clarke, a professor at the Jackson School. “Different groups shifted to plant-dominated or mixed diets. This shift likely led to changes in coloration of skin and non-feather tissues.”
In addition to coloring the past, the research puts living birds in a new perspective. Davis says that the bird groups examined in the study have a reputation for being drab—especially in comparison to songbirds, which researchers excluded from the study because they are the most distantly related to their non-avian dinosaur ancestors.
But aside from their feathers, the birds turned out to be quite colorful. The study found that about 54% of the 4,022 bird species studied had bright colors. Of this group, 86% of species expressed bright color in only non-feathered tissues.
The study provides important insights on bird color that often go overlooked, says Mary Caswell Stoddard, an associate professor at Princeton University.
“There is so much more to birds’ color than their plumage—just think of the vibrant orange-yellow bill of a toco toucan—but feathers tend to get the most attention,” she says. “This study unravels the evolutionary history of carotenoid-based coloration not just in plumage but also in the beaks and skin of birds and their relatives.”
The study appears in the journal Evolution. The National Science Foundation and the Jackson School funded the work.
Source: University of Texas at Austin


