Examining the spines of Neanderthals may explain the back pain and related ailments that humans today experience, new research shows.
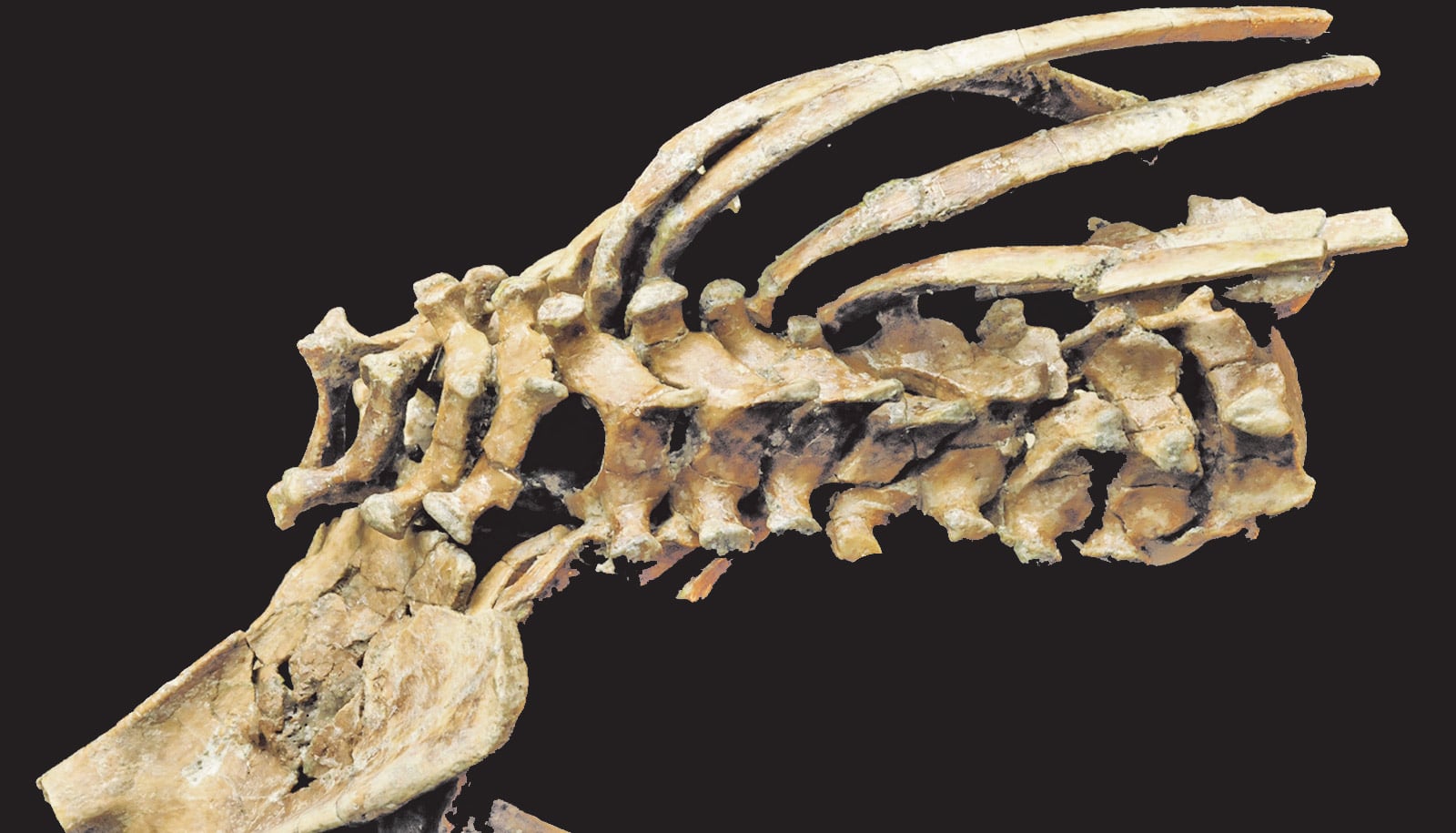
The analysis centers on the spine’s curvature, which results from, in part, a wedging, or angling, of vertebrae and the intervertebral discs—the softer material between the vertebrae.
“Neanderthals are not distinct from modern humans in lumbar wedging and therefore likely possessed curved lower backs like we do,” says Scott Williams, an associate professor in New York University’s anthropology department and a coauthor of the paper in PNAS Nexus.
“However, over time, specifically after the onset of industrialization in the late 19th century, we see increased wedging in the lower back bones of today’s humans—a change that may relate to higher instances of back pain, and other afflictions, in postindustrial societies.”
Researchers have long thought Neanderthals had a different posture than modern humans.
“A good part of this perspective derives from the wedging of Neanderthals’ lumbar, or lower, vertebrae—their spines in this region curve less than those of modern humans studied in the US or Europe,” Williams says.
However, much of this view was based on an analysis of modern humans beginning in the late 19th century—well after the onset of industrialization, which significantly altered our daily lives.
Furniture, for instance, became more widely available and desk jobs more prevalent—both of which encouraged sitting and, with it, changes in posture. These changes were coupled with a reduction in high-activity occupations, such as agriculture. In addition, specific afflictions became associated with working conditions that elicit poor posture.
“Past research has shown that higher rates of low back pain are associated with urban areas and especially in ‘enclosed workshop’ settings where employees maintain tedious and painful work postures, such as constantly sitting on stools in a forward leaning position,” Williams says.
In other words, by examining spines from humans who lived in the post-industrial era, past researchers may have mistakenly concluded that spine formation is due to evolutionary development rather than changed living and working conditions.
To address this possibility, Williams and colleagues examined both pre-industrial and post-industrial spines of male and female modern humans from around the world—a sample that included more than 300 spines, totaling more than 1,600 vertebrae—along with samples of Neanderthal spines.
Overall, they found that spines in post-industrial people showed more lumbar wedging than did those in pre-industrial people. Moreover, Neanderthals’ spines were significantly different from those in post-industrial people but not from pre-industrial people. Notably, the scientists found no differences linked to geography within samples from the same era.
“A pre-industrial vs. post-industrial lifestyle is the important factor,” explains Williams, who acknowledges that because lower back curvature is made up of soft tissues (i.e., intervertebral discs), not just bones, it cannot be ascertained that Neanderthals’ lumbar lordosis differed from modern humans.
“The bones are often all that is preserved in fossils, so it’s all we have to work with,” he adds.
Nonetheless, the distinctions in spine formation between pre-industrial and post-industrial humans offer new insights into back conditions facing many today.
“Diminished physical activity levels, bad posture, and the use of furniture, among other changes in lifestyle that accompanied industrialization, resulted, over time, in inadequate soft tissue structures to support lumbar lordosis during development,” Williams says.
“To compensate, our lower back bones have taken on more wedging than our pre-industrial and Neanderthal predecessors, potentially contributing to the frequency of lower back pain we find in post-industrial societies.”
Monica Alivez, a doctoral student and Saul Shukman, an undergraduate student, both at NYU, are coauthors of the paper. Additional coauthors are from the University of Johannesburg, Texas A&M University, the New York Institute of Technology, Arizona State University, and Chaffey College.
Source: NYU