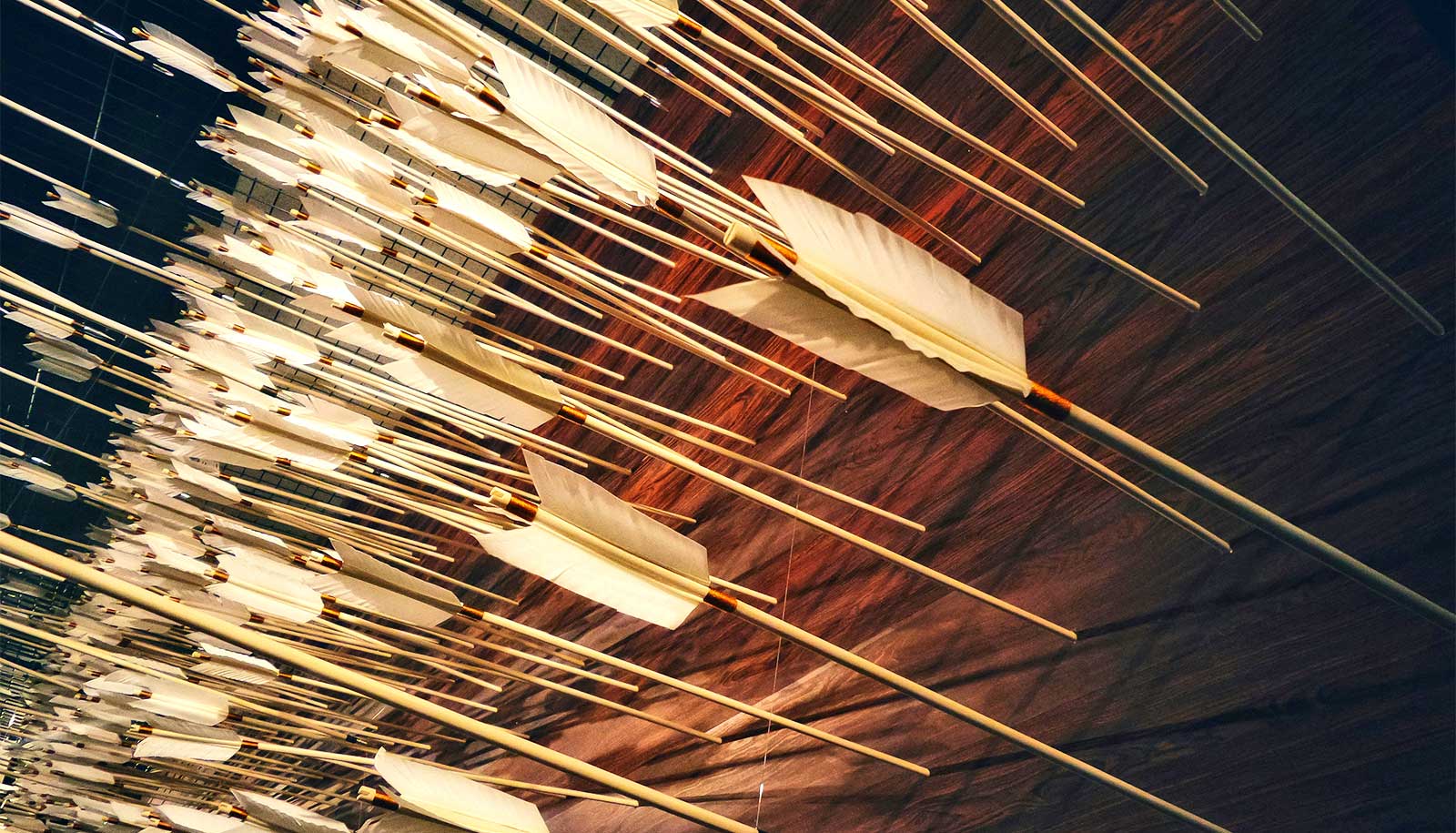
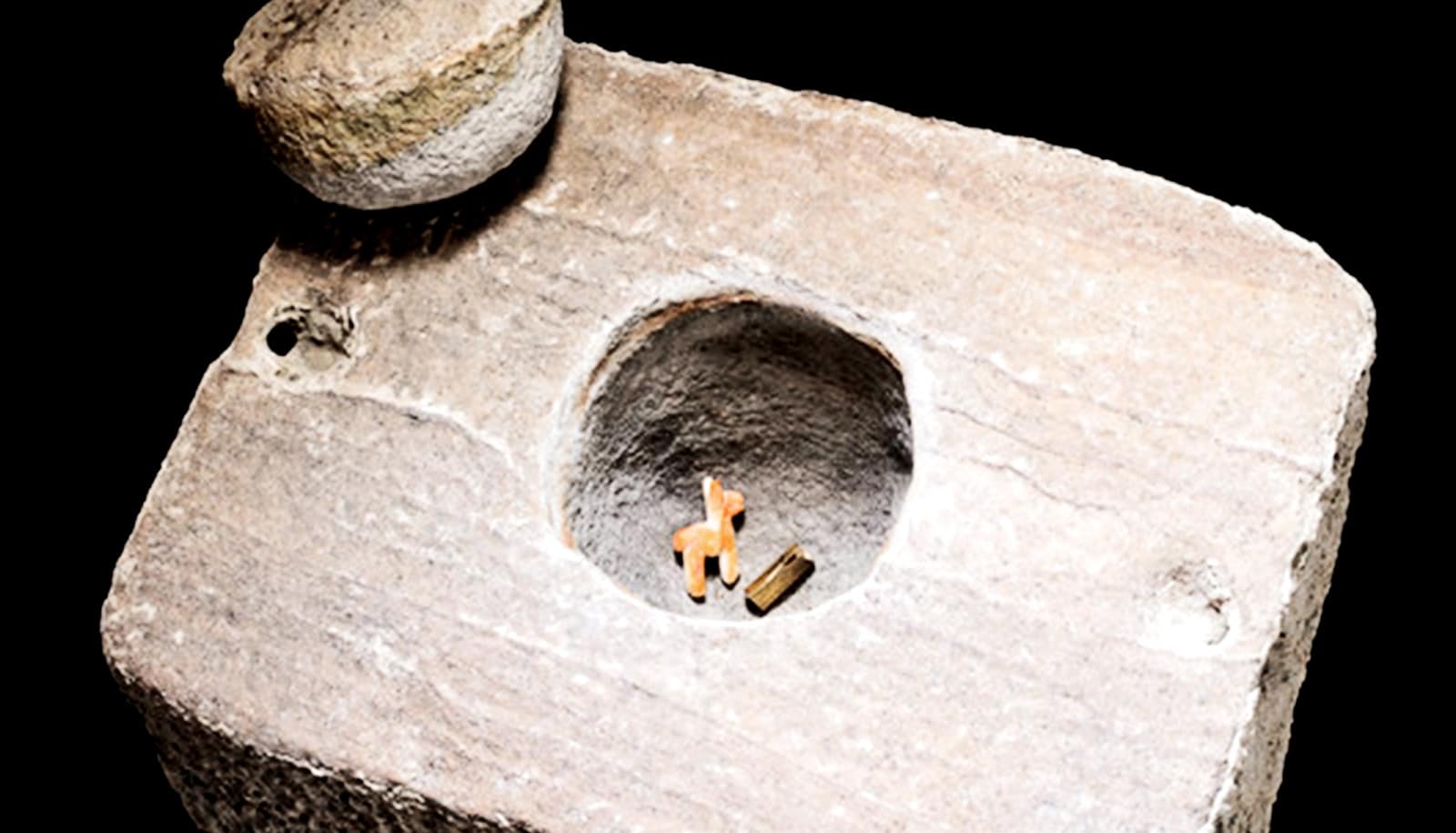
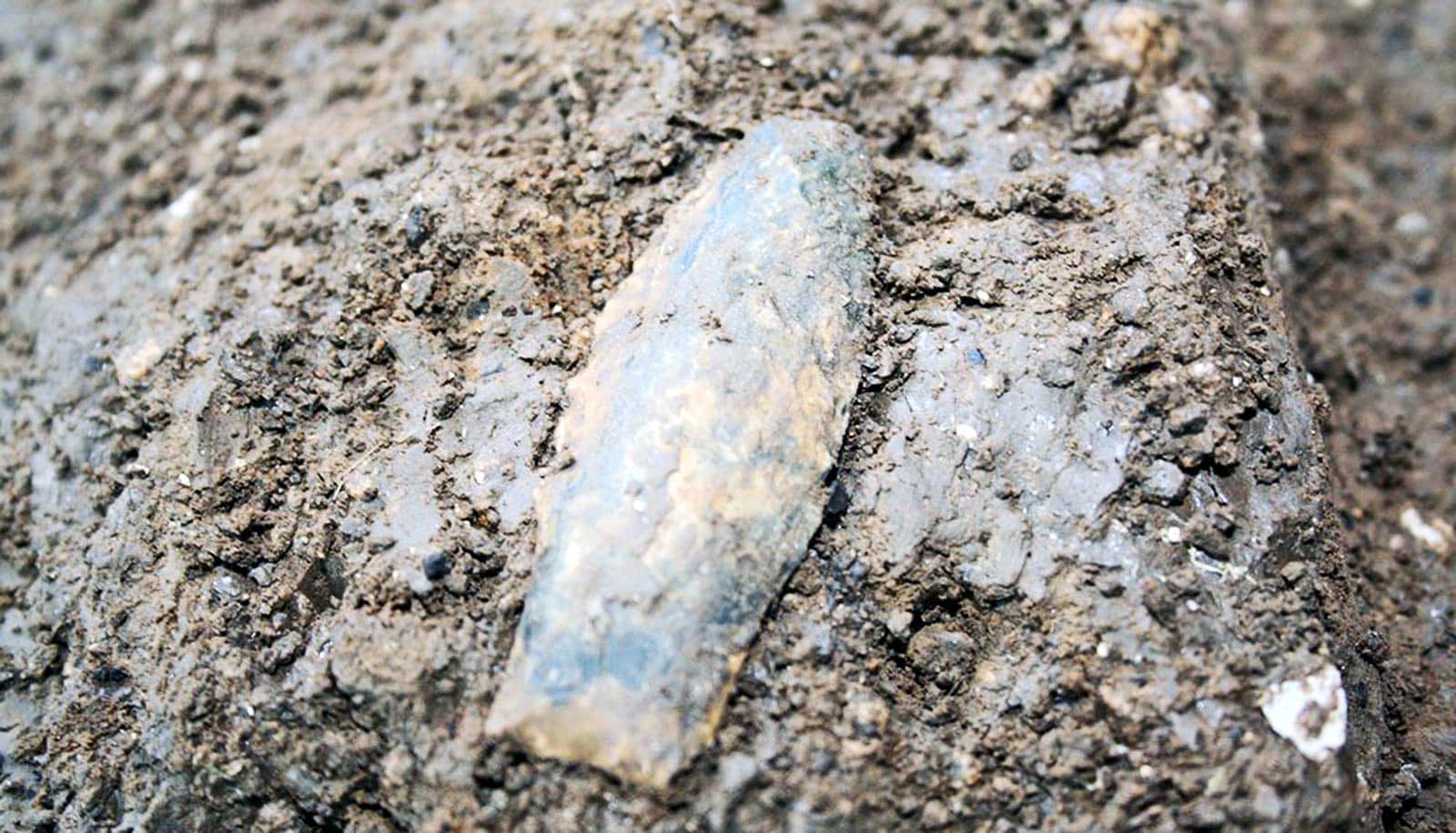
People in the Americas started to use bow and arrows around 5,000 years ago, according to a new study.
The research indicates that adoption of the technology coincided with the both the expansion of exchange networks and the growing tendency for people to reside in villages.
When archery arose in the Americas and the effects of the technology on society have long been debated among anthropologists and archaeologists. The new findings shine light on the mystery.
Focusing on the Lake Titicaca Basin in the Andes mountains, anthropologists found through analysis of 1,179 projectile points that the rise of archery technology dates to around 5,000 years ago. Previous research held that archery in the Andes emerged around 3,000 years ago.
“We think our paper is groundbreaking because it gives us a chance to see how society changed throughout the Andes throughout ancient times by presenting a huge number of artifacts from a vast area of South America,” says Luis Flores-Blanco, an anthropology doctoral student at the University of California, Davis and corresponding author of the paper published in the journal Quaternary International.
“This is among the first instances in which Andean archaeologists have investigated social complexity through the quantitative analysis of stone tools.”
Researchers say increasing social complexity in the region is usually investigated through analysis of monumental architecture and ceramics rather than projectile points, which are historically linked to foraging communities.
For the study, the team examined more than a thousand projectile points created over 10,000 years. Each projectile point originated in the Lake Titicaca Basin, specifically the Ilave and Ramis valleys, which are located southwest and northwest of the basin, respectively.
It’s among the highest plateau lands explored and conquered by humans, with Lake Titicaca sitting at an elevation of 12,500 feet, Flores-Blanco says.
“At Titicaca, Andeans accomplished the remarkable achievement of domesticating plants like the potato, leaving behind a nutritious legacy that is still appreciated today,” he says. “On top of that, the Tiwanaku were one of the major Andean civilizations that built their vast territory here. Even the Inca Empire claimed this territory was their mythical place of origin. Our study digs even deeper and goes to the roots of this Andean civilization.”
In their analysis, Flores-Blanco and his colleagues considered each projectile’s date of origin and then measured its length, width, thickness, and weight. They noticed that older projectile points—from the Early Archaic through the Late Archaic—were larger. A significant decrease in size occurred during the Terminal Archaic period, around 5,000 years ago. The team hypothesized that this size shift indicates a change in preference from spear-throwing technology to bow-and-arrow technology, but without abandoning the old technologies.
In addition, the team compared their projectile data to archaeological data from the region concerning settlement sizes, raw material availability and cranial trauma data. During the Terminal Archaic period, settlement sizes increased but the total number of settlement sites decreased, the researchers say. Not only that, but the inhabitants lacked signs of social violence, even though they had access to exotic raw materials.
“Based on our discovery, we can suggest that bow-and-arrow technology could have maintained and ensured adherence to emerging social norms that were crucial, such as those observed in the development of new social institutions, like obsidian exchange hubs or among individuals establishing residence in expanding villages,” Flores-Blanco says.
Additional coauthors are from UC Davis, the National University of San Marcos, UC Merced, the University of South Florida, and the University of Wyoming.
Source: Greg Watry for UC Davis