Data from social media websites like Facebook could supplement US census data, particularly for information about migrant populations, a new study suggests.
Determining how many people live in Seattle, perhaps of a certain age, perhaps from a specific country, is the sort of question that finds its answer in the census, a massive data dump for places across the country.
But just how fresh is that data? After all, the census updates once a decade, and the US Census Bureau’s smaller but more detailed American Community Survey updates annually. There’s also a delay between data collection and publication. (The release of data for 2016 started gradually in September 2017.)
The new study demonstrates how present-day migration statistics can be obtained by compiling the same data that advertisers use to target their audience on Facebook, and by combining that source with information from the Census Bureau.
Digging into the databases
Migration indicates a variety of political and economic trends and is a major driver of population change, says Emilio Zagheni, an associate professor of sociology at the University of Washington who led the study.
As researchers further explore the increasing number of databases produced for advertisers, Zagheni argues, social scientists could leverage Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter more often to glean information on geography, mobility, behavior, and employment.
While there are some limits to the data—each platform is a self-selected, self-reporting segment of the population—the number of migrants according to Facebook could supplement the official numbers logged by the US Census Bureau, Zagheni says.
“Facebook data are freely available and disaggregated at the level of city or ZIP code in the US,” Zagheni says.
“Is it better to have a large sample that is biased, or a small sample that is nonbiased?”
The study focused on Facebook’s Ads Manager service, which allows users, in the interest of placing an ad, to input information on a target audience—information about which the platform then generates data. As an example, researchers identified an audience for a hypothetical ad aimed at Italian expatriates living in Washington state; Facebook reported approximately 3,800 monthly active users in that audience. (That data input process is free; taking it a step further to launch an ad carries a cost.)
Scientists studying migration trends—say, where different groups have located in the United States—could turn to the Facebook Ads Manager tool. But it’s important to recognize biases in the data and some ambiguity in the way migration is measured, Zagheni says.
The American Community Survey, in contrast, is the modern incarnation of the old census “long form,” randomly sent to US households annually to collect not only demographic information, but also statistics on housing, jobs, and other socioeconomic trends.
Comparing the numbers
In the study, Zagheni and his colleagues developed a computer program for extracting data from Facebook Ads Manager about expats from more than 50 countries to every US state, disaggregated by age and sex.
The team mined data from a platform of more than 1.8 billion users worldwide, drawing on an innovative statistical model that researchers set up to adjust for the data’s typical shortcoming: Facebook users are not representative of the entire underlying population.
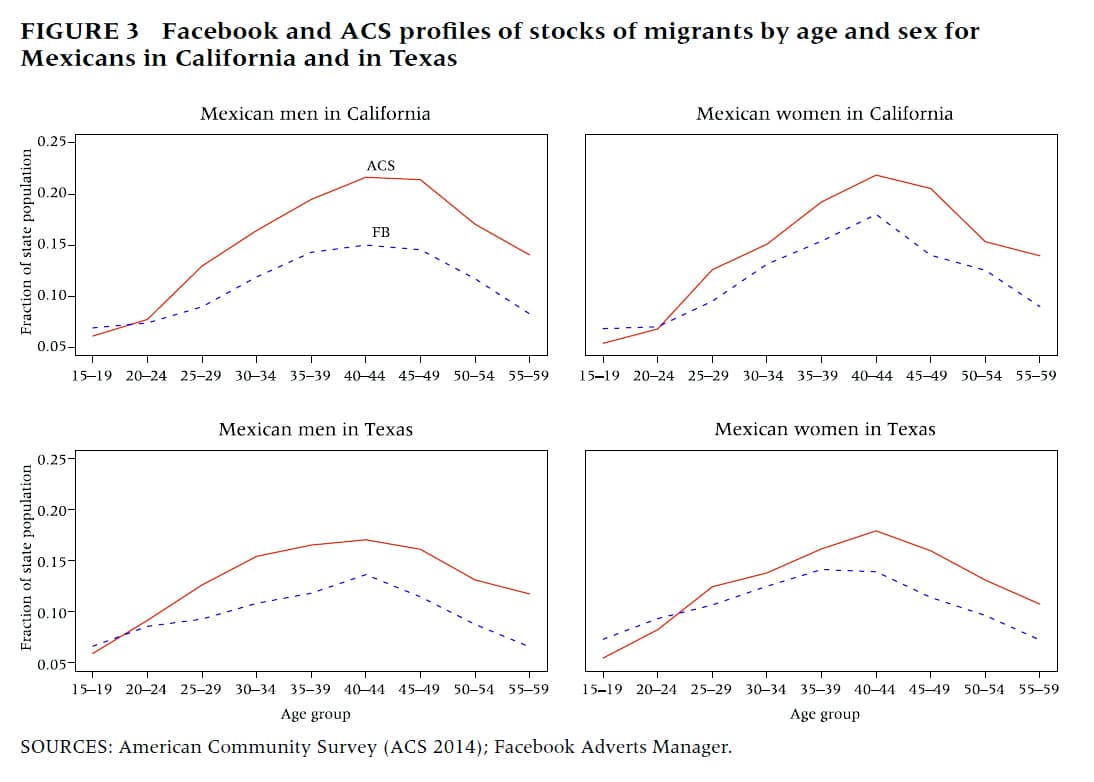
As an illustrative example, Zagheni and colleagues compared the numbers of Mexicans living in California and Texas, by age and sex, with the numbers compiled by the American Community Survey. The researchers did the same with the estimates of immigrants from the Philippines to both states.
The team found that, generally speaking, the numbers of Mexican migrants in California and Texas estimated by Facebook were noticeably lower than the numbers reported by the American Community Survey, particularly among older Mexicans. The American Community Survey, for instance, estimates that Mexican-born men ages 40 to 44 represent more than 20 percent of California’s population of men in that age range; Facebook puts the proportion at closer to 15 percent.
US Census may have missed 400,000 Hispanic kids
Those discrepancies could reflect biases in the data, Zagheni says, such as lower Facebook usage in that demographic group, or differences across age groups in the amount of information posted on Facebook, such as details about users’ hometowns—and thus whether they would be considered an expat.
For immigrants from the Philippines, the differences between Facebook and American Community Survey estimates are narrower, with a potential overestimate of older Filipinos in both states. In Texas, for example, Facebook estimates Filipinos ages 50 to 54 represent 5 percent of the state’s male population in that age range, whereas the American Community Survey estimate is closer to 2.5 percent.
Bias vs. sample size
Zagheni and colleagues worked on identifying such biases in the Facebook data, and their similarities among groups or across states. They then developed a model that allows researchers to make adjustments by combining information from Facebook and the American Community Survey.
“Is it better to have a large sample that is biased, or a small sample that is nonbiased? The American Community Survey is a small sample that is more representative of the underlying population; Facebook is a very large sample but not representative,” Zagheni says.
“The idea is that in certain contexts, the sample in the American Community Survey is too small to say something significant. In other circumstances, Facebook samples are too biased. With this project we aim at getting the best of both worlds: By calibrating the Facebook data with the American Community Survey, we can correct for the bias and get better estimates,” says Zagheni.
Do friends give your data to third-party apps?
The next step, he adds, is to test the approach in developing countries, where timely and reliable statistics are important for development.
Zagheni received support from the Washington Research Foundation, the eScience Institute, and the Center for Studies in Demography and Ecology at the University of Washington. Additional coauthors are from the Qatar Computing Research Institute in Qatar, and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems in Germany.
The researchers report their findings in the journal Population and Development Review.
Source: University of Washington



